by Anaswara.J.S.(2016-2019)
anaswarajs@gmail.com

Computers of various sorts play a role in many processes of modern society. A prominent example is the personal computer which has a specific user interface, waiting for human input and delivering output in a prescribed format. Computers also feature in automated processes, for example in the production lines of a modern factory. Here the input/output interface is usually with other machinery, such as a robot environment in a car factory.
An increasingly important role is played by so-called
intelligent agents that operate autonomously in more complex and changing environments. Examples of such environments are traffic, remote space, but also the internet. The design of intelligent agents, specifically for tasks such as learning , has become a unifying agenda of various branches of artificial intelligence . Intelligence is defined as the capability of the agent to perceive and act on its environment in a way that maximizes its chances of success. In recent years, the field of embodied cognitive sciences has provided a new conceptual and empirical framework for the study of intelligence, both in biological and in artificial entities.
A particular manifestation of intelligence is creativity.Creativity is understood as a distinguished capability of dealing with unprecedented situations and of relating a given situation with other conceivable situations.

Artificial agent designs quantum experiments
We carry smartphones in our pockets, the streets are dotted with semi-autonomous cars, but in the research laboratory experiments are still being designed by people. However, this could change soon. . For this purpose, projective simulation model for artificial intelligence can be used which enable a machine to learn and act creatively. The memory of this autonomous machine stores many individual fragments of experience, which are networked together. The machine builds up and adapts its memories while learning from both successful and unsuccessful experience. Quantum experiments are an ideal environment to test the applicability of AI to research.

Optimized experiments designed by an AI-agent
All starts with an empty laboratory table for photonic quantum experiments. The artificial agent then tries to develop new experiments by virtually placing mirrors, prisms or beam splitters on the table. If its actions lead to a meaningful result, the agent has a higher chance to do similar sequence of actions in the future. This is known as a reinforcement learning strategy. The artificial agent performs tens of thousands of experiments on the virtual laboratory table. When we analyze the memory of the machine, we can discover that certain structures have developed. Some of these structures are already known to physicists as useful tools from modern quantum optical laboratories. Others are completely new and could, in the future, be tested in the lab. “Reinforcement learning” is what allows us to find, optimize and identify a huge amount of potentially interesting solutions.

Creative support in the laboratory
In the future, the scientists want to further improve their learning program. At this point, it is a tool that can autonomously learn to solve a given task. But can a machine be more than a tool? Can it provide more creative assistance to the scientists in basic research? This is what the scientists want to find out and only the future can tell what answers are in store for them.
Artificial intelligence

Artificial intelligence ( AI, also machine intelligence , MI ) is intelligence displayed by machines, in contrast with the natural intelligence ( NI ) displayed by humans and other animals. In computer science AI research is defined as the study of ” intelligent agents”: any device that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its chance of success at some goal.
Projective simulation model for artificial intelligence

A learning agent whose interaction with the environment is governed by a simulation-based projection, which allows the agent to project itself into future situations before it takes real action. Projective simulation is based on a random walk through a network of clips, which are elementary patches of episodic memory. The network of clips changes dynamically, both due to new perceptual input and due to certain compositional principles of the simulation process. During simulation, the clips are screened for specific features which trigger factual action of the agent. The scheme is different from other, computational, notions of simulation, and it provides a new element in an embodied cognitive science approach to intelligent action and learning. Our model provides a natural route for generalization to quantum-mechanical operation and connects the fields of reinforcement learning and quantum computation.
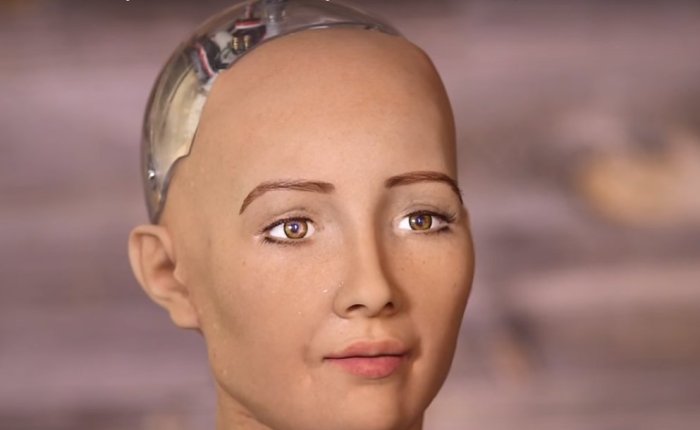
 In October 2017, Sophia became a Saudi Arabian citizen, the first robot to receive citizenship of any country. In November 2017, Sophia was named the united nations development programme’s first ever Innovation Champion, and the first non-human to be given any United Nations title.
In October 2017, Sophia became a Saudi Arabian citizen, the first robot to receive citizenship of any country. In November 2017, Sophia was named the united nations development programme’s first ever Innovation Champion, and the first non-human to be given any United Nations title. 