by Abhijith.A.D(2016-2019)
https://www.facebook.com/abhijith.vjmd
Electromagnetism
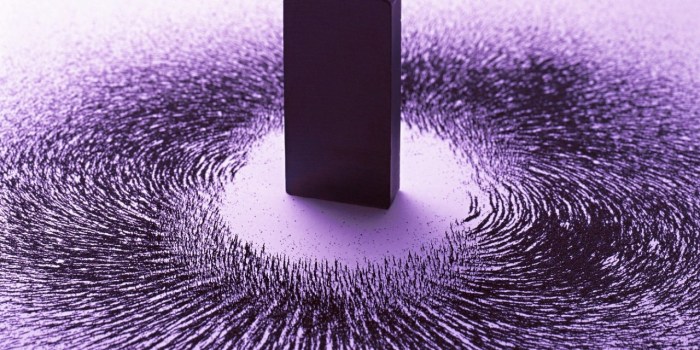
Electromagnetism is a branch of physics involving the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually exhibits electromagnetic fields such as electric fields, magnetic fields and light, and is one of the four fundamental interactions (commonly called forces) in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation.
Lightning is an electrostatic discharge that travels between two charged regions.
The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον ēlektron, “amber“, and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means “Μagnesian stone”, a type of iron ore. Electromagnetic phenomena are defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called theLorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as different manifestations of the same phenomenon.
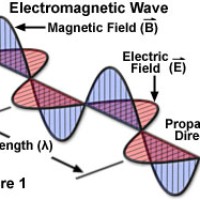
The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual atoms and molecules in matter, and is a manifestation of the electromagnetic force.Electrons are bound by the electromagnetic force to atomic nuclei, and their orbital shapes and their influence on nearby atoms with their electrons is described by quantum mechanics. The electromagnetic force governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms.

There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current. In Faraday’s law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell’s equationsdescribe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.
The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, particularly the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the “medium” of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.
Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch the unified force broke into the two separate forces as the universe cooled.
Electronics
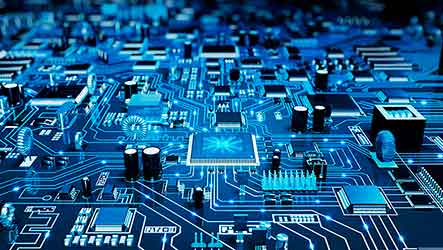
Electronics is the science of controlling electrical energy electrically, in which the electrons have a fundamental role. Electronics deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components (such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes, integrated circuits, optoelectronics, and sensors), associated passive electrical components, and interconnection technologies. Commonly, electronic devices contain circuitry consisting primarily or exclusively of active semiconductors supplemented with passive elements; such a circuit is described as an electronic circuit.
The science of electronics is considered to be a branch of physics and electrical engineering.

The nonlinear behaviour of active components and their ability to control electron flows makes amplification of weak signals possible. Electronics is widely used in information processing, telecommunication, and signal processing. The ability of electronic devices to act as switches makes digital information processing possible. Interconnection technologies such as circuit boards, electronics packaging technology, and other varied forms of communication infrastructure complete circuit functionality and transform the mixed components into a regular working system.
Electronics is distinct from electrical and electro-mechanical science and technology, which deal with the generation, distribution, switching, storage, and conversion of electrical energy to and from other energy forms using wires, motors, generators, batteries, switches, relays, transformers, resistors, and other passive components. This distinction started around 1906 with the invention by Lee De Forest of the triode, which made electrical amplification of weak radio signals and audio signals possible with a non-mechanical device. Until 1950 this field was called “radio technology” because its principal application was the design and theory of radio transmitters, receivers, and vacuum tubes.

Today, most electronic devices use semiconductor components to perform electron control. The study of semiconductor devices and related technology is considered a branch of solid-state physics, whereas the design and construction of electronic circuits to solve practical problems come under electronics engineering. This article focuses on engineering aspects of electronics.
 NORTHERN LIGHTS
NORTHERN LIGHTS